Exchange Rates Can Be Explained by Different Underlying Theories
If there was greater demand for Pound Sterling it would cause the value to increase. Fixed exchange rates including the elasticity approach and the absorption.
Traditional theories developed during the period of.
. Similarly Keith Pilbeams explanation amounts to economic fundamentals are de-rived from modem exchange rate models Pilbeam 1994 p. US consumer price index CPI. Long run means in this context a general macroeconomic equilibrium with full.
Through a change in the nominal exchange rate E. Higher interest rates make it more attractive to save in the UK therefore more investors will switch to British. Practitioners use structural model to generate equilibrium exchange rates.
And Taylor calls the Fundamentals those variables derived from the four major exchange rate models based on conventional macro fundamen-. To reduce in value over time. Power parity theory of exchange rates PPP.
The real exchange rate is equal to the nominal exchange rate E the price of domestic currency in terms of foreign currency times the domestic price level P divided by the domestic price level P. The rise in domestic interest rates are usually followed by the appreciation of domestic currency and a reduction in domestic interest rates follow the devaluation of national currency. Countries have a vested interest in the exchange rate of their currency to their trading partners currency because it affects trade flows.
Hence the level of the exchange rate matters for the economys cyclical position output gap. This article throws light upon the three theories of determination of foreign exchange rates. Mint Parity theory 2.
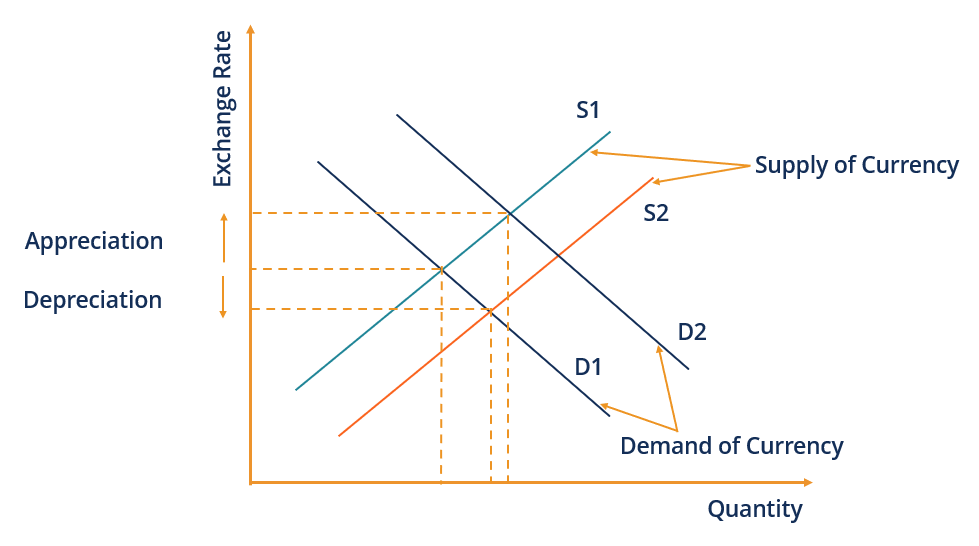
By the time the gold standard monetary policymakers have concluded that changes in exchange rates are influenced by monetary policy. Typically exchange rates can be free-floating or fixed. This increase in demand for US goods would cause an appreciation increase.
A free-floating exchange rate rises and falls due to changes in the foreign exchange market. A trading signal can be generated every time there is a significant difference between the model-based expected or forecasted exchange rate and the exchange rate observed in the market. A fixed exchange rate is pegged to the value.
Purchasing Power Parity Theory 2. Balance of payments theory. Nomic theory MacDonald and Taylor 1992 p.
Exchange rate theories traditional approach also called the trade or elasticities approach. Purchasing power parity theory 3. Where it occurs above BP giving a payments surplus the exchange rate will appreciate.
This can only be. Based on flow of goods services. Determination of Exchange Rates.
Theories of exchange rates determination have changed since the exchange rate system. Where equilibrium occurs below BP giving a payments deficit the exchange rate will depreciate. Different theories have been developed to explain the determination of rate of exchange.
With flexible exchange rates a position of equilibrium as represented by a point of intersection between IS and LM which lies off the BP schedule will result in a change in the exchange rate. Exchange rates and Competitiveness An appreciating exchange rate is usually thought to be contractionary and deflationary. The equilibrium exchange rates can be used for projections or to generate trading signals.
An exchange rate is determined by the supply and demand for the currency. This theory is partially replaced by a novel quite unusual approach coined general model of long-run exchange rates pp. Shifted to the floating rates system.
Mint parity theory explains the determination of exchange rate between the two gold standard countries. Both nominal and real exchange rates can be expressed as a geometric or arithmetic trade weighted index between multiple countries rather than ju st between two countries so-called bi-lateral exchange. An appreciation in the exchange rate could occur if the UK has.
Exchange rate is an exponentially weighted average of expected future dif- ferences between the logarithms of the nominal money supply and the exogenous component of money demand. Other Determinants of Exchange Rates. Assumes an equilibrium exchange rate where the imports balances the exports of the country.
Exchange rate theories 1. If US business became relatively more competitive there would be greater demand for American goods. Exchange rates are determined by factors such as interest rates confidence the current account on balance of payments economic growth and relative inflation rates.
A depreciating exchange rate is usually thought to be expansionary and inflationary. A theory of long-term equilibrium exchange rates based on relative price levels of two countries. There are therefore two ways in which the real exchange rate can adjust.
A higher exchange rate can be expected to worsen a countrys balance of trade while a lower exchange rate can be expected to improve it. Interest Rate Theories 3.
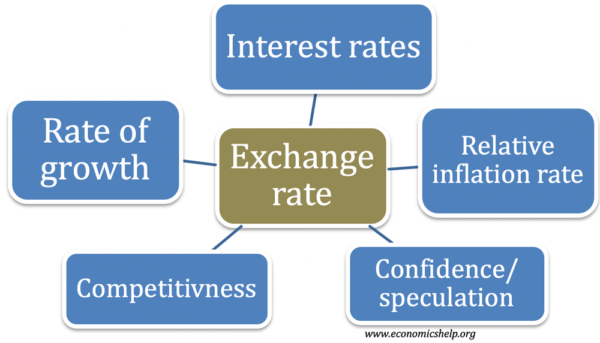
Factors Which Influence The Exchange Rate Economics Help

Infographic How Banks Can Influence The Currency Exchange Rate Exchange Rate Foreign Currency Trading Currency

Floating Exchange Rate Overview Functions Benefits Limitations
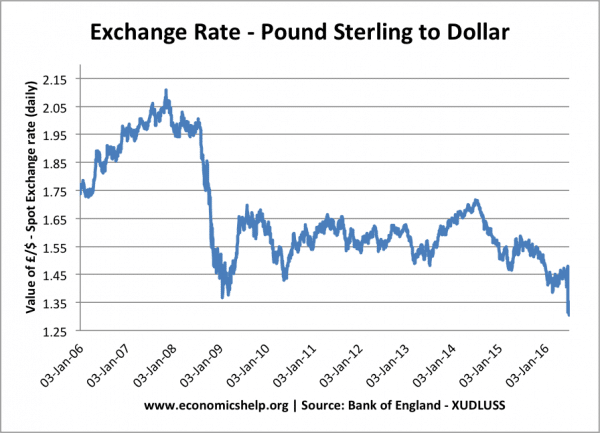
0 Response to "Exchange Rates Can Be Explained by Different Underlying Theories"
Post a Comment